
Effective management of a team and perfect coordination between members of the team to achieve a common goal and complete a task is called project management (PM). The use of tools, techniques, skills, and knowledge comes into play in project management. Adequate planning, scheduling, and monitoring of all the activities will ensure the project’s success. However, for all of the above to happen in synchronization, one also needs to understand the basic topics and discussions that include: the project process, project lifecycle, and project management system. So, let us start at the beginning and learn about project management.

What is Project Management?
A project is an effort made to deliver a unique product or service. It involves a definite start and end. The goal of any project is significant and monitored by a professional working as a project manager and concludes upon achieving the goal. The outcome of the project could be temporary. A group of projects managed to enhance productivity and efficiency is a program. A portfolio is a group of programs aligned to suit organizational goals, values, and strategies.
What is Operational Work?
An organization can have either project work or operational work. Operational work is the maximum work done in enterprises and is always ongoing, whereas project work has a substantial completion.
Elements of Project Management
Each project is unique. The unique nature of projects leads to many possibilities and uncertainties that may bring negative, positive, or neutral results.
New issues arise during project development each day, which could risk the project’s progress. Thorough knowledge of project management basics will help you overcome any challenge.
The following key elements will provide a greater chance of success:
Value of Project Management
Professional project managers must be very responsive to the intricacy and responsibilities of project management. Though PM seems exciting, it comes with its challenges. To be successful at a PM job, you require not only skills but also knowledge of project management basic concepts.
To make this possible, you must imbibe some important project management values, as illustrated in the graphic below.
Categories Within Project Management
Fundamentals of project management also demand a comprehensive knowledge of ten core areas. Once you understand and follow these categories, you can rest assured that your projects will run smoothly with few- if at all-technical hitches.
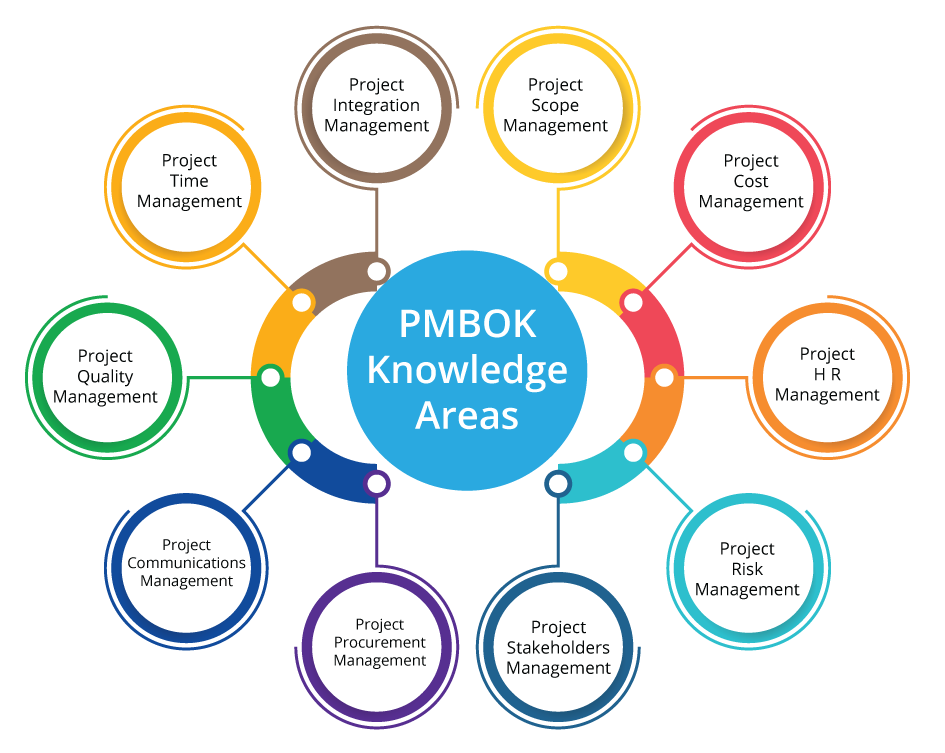
Here is a closer look at these areas to get a better perspective of PM.
-
-
Project Integration Management
Part of project management basics, this area of PM holds together all the individual tasks and processes in a single project with specific goals and deliverables. Good project integration is unthinkable without a worthy team. To be efficient in project execution, you should have superior human resources – people who are responsive to roles and responsibilities. However, the onus of adhering strictly to the project objectives lies with the project manager. While focusing on the bigger picture, a strategic approach will help to identify problems and fix them quickly before the project is affected.
-
Project Scope Management
The process of defining and documenting the project falls under project scope management. Anyone who knows project management basic concepts would be aware that lack of focus will push a project outside its scope. The concept of project scope management is to understand “what is” and “what is not” included in the project.
-
Project Time Management
Completing projects within the deadline can be a challenging task for project managers. However, it is integral to the fundamentals of project management, and there can be no compromise on this. This area of PM is concerned with estimating the time required for accomplishing project activities, planning a project schedule, and controlling and monitoring deviations. It keeps project activities on track and monitors the activities against the PM plan to make sure the project meets deadlines.
-
Project Cost Management
Cost management is all about handling project related finances. Project managers should know that sticking to the budget is part of project management basics. It is better to draw up a list of expenditures, carry out a cost-benefit analysis, effect changes if required, and only then launch the project. Without effective cost management techniques, it is not possible to complete the project within the specified budget. Remember, it may also be possible to save on the budget allocated. If you cannot foresee how much your project costs, then how will you be able to quantify the profit gained?
-
Project Quality Management
The term “quality” is not the same as “perfection”. It is not reasonable to spend time and resources to take your project to perfection. No matter how you define the term quality, only a high-quality project gratifies customer expectations without any insufficiencies.
-
Project Human Resources Management
The management of human resources in a project – taught as one of the most important project management basic concepts – is, in reality, the most neglected area. You need to understand the kind of resources required to execute the project successfully and then organize your team accordingly. Human resource is all about the way you handle the most valuable asset of the company, i.e., employees. To be successful, project managers should have a clear idea of the requirements before hiring and place only the right candidates who can handle the project competently. Only the right people in the right places can improve the odds of success.
-
Project Communication Management
Though all the areas are equally essential, communication is regarded as supreme as it provides information about every aspect of the project. Regular and effective communication that enhances team spirit is among the important fundamentals of project management.
-
Project Risk Management
No project runs smoothly without any technical hitches; so it would be unrealistic to assume that everything will fall in place. Always factor in the unexpected, a last minute problem or an irritating snag. Such risk management is part of project management basics. You predict and prepare for trouble. Risk management plays a vital role in preventing failure. Ignoring minor risks leads to project failure as a minor risk can turn into a major risk. If left unattended, it can lead to project disaster.
-
Project Procurement Management
This area includes all the facets of purchase and acquisition of products and services that are essential for efficient project completion. While the procurement process is transparent and conducted through agreement, it is crucial for project managers to validate the same and ensure that there are no inconsistencies. No matter whether you are a seller or buyer, you should cultivate the ability to understand issues from both viewpoints. Though this particular PM area may not be of use routinely, it is very much a part of project management basic concepts and, you can draw exceptional value by using it right.
-
Project Stakeholder Management
Project stakeholder management is the final knowledge area and considered very important. The success or failure of the product depends on timely and satisfactory project delivery to stakeholders.
-
Who Exactly are the Stakeholders?
- Stakeholders are not merely clients who have entrusted you with a project. They include team members involved in the project, suppliers, customers-a merry mix of people who belong to both the internal and external work environment of an organization.
Implementing the fundamentals of project management within your project will prevent the need for crisis management. It will help you move ahead, taking proactive decisions on the way. As you start implementing the above project management basics, you will become a master at managing the projects and the people involved in taking the project to completion.
Project Management Concepts
However, do not forget three project management concepts:
- Project Process: An administrative process to plan and control project implementation;
- Project Lifecycle: A four-stage framework including initiation, planning, execution and closure to manage a project well;
- Project Management Systems: A suite of general and project management software applications to help in executing a project.
Organizational Project Management and Project Management
The current business scenario is continually changing to synchronize with changing market conditions and customer requirements. The change might affect various parts of the project owing to its nature and complexity. To overcome this issue, “Organizational Project Management” (OPM) is implemented and is in tune with project management basic concepts.
What is OPM?
OPM is the efficient management of projects, processes, and programs in line with the company’s strategic goals. It is a permutation of profile management, program management, and PM.
The major objective of OPM is to translate its vision and mission into detailed actions that deliver maximum value to the stakeholders, be it beneficiaries or donors. Accomplishing this ensures continuous growth and a viable competitive advantage. It is most true in the prevailing competitive global work environment, where enterprises are persistently looking ahead to advance their capabilities and enhance their performance.
Project-based management is a way of thinking about running a business. It’s a mental framework for running a company. Organizational goals are established and met through the coordinated execution of several interdependent initiatives, such as those aimed at operational enhancement and transformation, as well as more conventional endeavors, such as new product creation. Thus, we can now see corporate project management.
User-Centered Design Principles
User-centered design is a set of processes or tools used to design a service that mainly satisfies what users require at the beginning of and through the development phase.
It helps to solve problems in a creative way; it starts with people and ends with solutions that are required to meet their pre-requisites. When you understand the target audience and design from their perspective, you will come up with ideas they will embrace. User-centric design is all about how you think and what you accomplish to satisfy users, according to project management basics.
Benefits of User-Centered Design Principles
The advantages of user-centered design are as follows:
- Increases Sales: Customers are more likely to purchase a product/service that caters to business requirements.
- Develops Positive User Experience: Customers will turn loyal, and your business will earn a good reputation.
- Increases Competitiveness: If your business products meet customer requirements, customers are less likely to pick other business products.
- Helps to Gain Business Insights: Gaining insights about business products or services could lead to the development of innovative products/services.
Also, the fundamentals of project management dictate involving customers in the design process to:
- Assist you in designing more efficient and safe products.
- Give a sense of ownership to the customers in the designing phase.
- Avoid changes to the design at a later phase while avoiding cost and time delays.
Project Charter
Under project management basic concepts, a project charter is a key document stating initial requirements of the project to meet stakeholder’s expectations. It involves outlining roles and responsibilities of the participants and describes the goals and objectives as well.
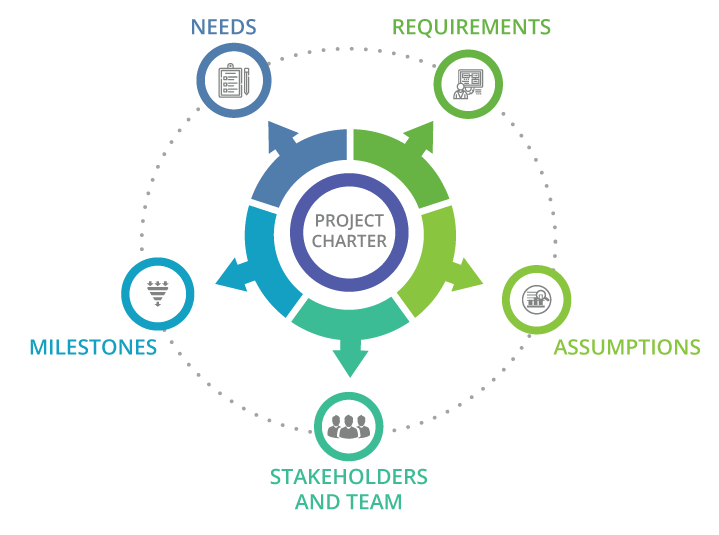
The project charter is an agreement between the organizations committed to producing a product/service and clients who receive the product. It gives a quick impression of the project as a whole. A project charter is usually created during the initiation stage and implemented in the project planning phase. Once a project charter is drawn up, it can neither be changed nor modified throughout the project lifecycle.
Think of a project charter as an unapproved project proposal and first deliverable of the project. It is used to secure stakeholders approval for accomplishing project goals. On approval of the project charter by the top management, the project manager prepares the project plan considering the approved project goals.
Project Plan
A project plan is a formally acceptable document that guides you on project control and execution. It also explains how to satisfy project objectives in terms of major products, milestones, resources, and activities required.
Project Charter Versus Project Plan
-
- Difference in Use A project plan ensures on-time and on-budget delivery of projects, whereas a project charter establishes a contract among stakeholders and shapes communication between the project team and top management.
- Difference in Application A project charter is primarily a sales document as it gives notice to the project committee for project approval, project structure, and framework. On the other hand, a project plan works on the approved structure of the project charter.
The project charter works as a pivot point all through the project execution phase and as a reference point to the project direction; a project plan, on the other hand, is a roadmap containing the detailed project execution process. Then, the experienced project manager determines the project’s actual progress as specified in the project plan.
Difference in Scope
A project charter is usually a summarized document which contains:
- Reasons for taking up the project
- Project budget and other related constraints
- Plausible solutions
- Risks and assumptions
- List of stakeholders including team members
- Role of all the team members
- Project structure
A project plan provides details on how to manage and deal with the controlled execution of the project, including:
- Roles and responsibilities of the people involved in the project
- The nature of work phases, tasks, and efforts required to meet the deliverables
- Resources allocation to meet deliverables
- Identification of work breakdown structure
- Project milestones and timelines
- The organizational structure
Creating a Schedule
Project scheduling is a process used to communicate what tasks need to get done and which organizational resource will be allocated to accomplish the task in the given time frame. The process should reflect the work required to deliver the projects on time. It is used all through the project management lifecycle.
A project schedule is an effective tool that helps project managers to communicate and collaborate with teams and stakeholders. Project managers greatly depend on project scheduling to prevent hitches. It is used to ensure that the project remains on the path.
An effective project schedule will help you manage time and resources. It also helps you determine the team’s capacity and identify a suitable person for each task.
A project schedule includes:
- Project deliverables
- Resources required in completing the task
- Dependencies between the tasks
- Task duration and project deadline
- The budget of the project
How to Create an Efficient Project Schedule?
Here is a quick guide on creating an effective project schedule:
-
- Define the Tasks The first step involved in creating a schedule is identifying the tasks that help you in completing the project. To do so initially, you should be able to ascertain all the deliverables to build an entire project. The deliverables are recognizable in the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
-
- On establishing the deliverables, create a list of tasks to be carried out for individual deliverables. Defining the tasks will avoid misperceptions on what has to be done to attain your goals before deadlines.
-
- Identify Dependencies Between the Tasks After listing the tasks, establish dependencies between the tasks. Do not overlook the types of dependency as it can affect the duration of the task as well as the entire project.
-
- Identify Resources Identifying resources available to deliver a project is very important as resources could be assigned to other projects simultaneously, which could lead to scheduling conflicts.
-
- Estimate Time After resource allocation, the very next step is to determine the task duration. The duration can spread to days, weeks, or months considering the project size and complexity. Under-estimation can impact the budget of the project and also adversely affect quality.
-
- Keep Project Schedule Updated Once the project starts, all your estimates change. Which is why you must keep your schedule up-to-date and data accurate. On completing the project schedule, it can be passed on to your manager.
Conclusion
Thus project management basics include various activities, some of them quite complex. Without thorough planning, it is difficult to attain specific goals.














